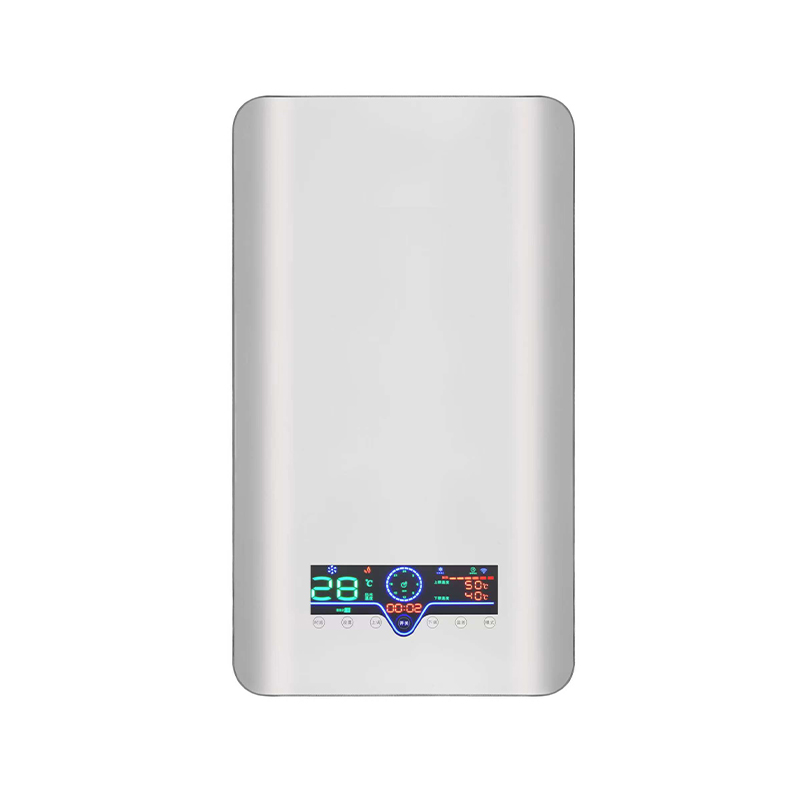
How does an arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace achieve precise, energy-efficient, and safe heat conversion?
Release Time : 2025-12-25
With the continuous evolution of modern industrial heating technology towards higher efficiency, cleaner operation, and greater intelligence, electromagnetic heating furnaces, with their advantages of non-contact heating, high energy efficiency, and low environmental impact, have been widely applied in various fields such as plastics machinery, chemical reactions, food processing, and metal heat treatment. Among them, the arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace is optimized for specific equipment shapes (such as cylindrical or curved workpieces like injection molding machine barrels and extruder barrels), demonstrating significant advantages in thermal efficiency, installation adaptability, and operational stability.
The core principle of the arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace is based on electromagnetic induction: when a high-frequency alternating current passes through an induction coil wound on an arc-shaped magnetic yoke, eddy currents are generated inside the metal load (such as a steel barrel) in front of it, thus directly converting electrical energy into heat energy. Because heat is generated inside the heated object, rather than through flames or resistance wires, heat loss is minimal, resulting in an energy utilization rate exceeding 90%, far higher than the 40%–60% of traditional resistance heating. Simultaneously, the entire process is flameless and produces no exhaust emissions, aligning with the development trends of green manufacturing and carbon neutrality.
The curved design is a key innovation of this type of equipment. The surface of a standard cylindrical workpiece is a continuous curved surface. Using a flat electromagnetic module would result in a gap between the coil and the cylinder wall, reducing magnetic coupling efficiency and potentially causing localized overheating or uneven heating. In contrast, the coil and yoke of the curved electromagnetic heating furnace are precisely pre-bent to the outer diameter of the cylinder, ensuring complete contact with the heated surface and maximizing the depth and uniformity of magnetic field penetration. This "tailor-made" structure not only improves heating efficiency but also reduces electromagnetic leakage, enhancing system safety.
In terms of material selection, arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces typically use high-permeability, low-loss nanocrystalline or ferrite cores as the yoke material, combined with high-temperature resistant mica plates, ceramic fibers, or silicone insulation layers to ensure electrical safety and structural stability during long-term operation above 300℃. The induction coils often use multi-strand Litz wire to effectively suppress the high-frequency skin effect, reduce AC resistance, and further improve energy efficiency. The outer casing is mostly made of aluminum alloy or stainless steel, combining heat dissipation, protection, and aesthetics.
The control system is also highly integrated. Modern arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces are generally equipped with intelligent temperature control modules that can collect the barrel temperature in real time and dynamically adjust the output power through PID algorithms to achieve temperature control accuracy within ±1℃. Some high-end models support multi-segment program settings, remote monitoring, fault self-diagnosis, and energy consumption statistics, facilitating integration with factory MES or industrial IoT platforms for digital management.
Ease of installation and maintenance is also one of the reasons for its popularity. Arc-shaped modules typically employ a segmented or snap-fit structure, allowing for quick installation onto existing equipment without disassembling the entire unit, significantly shortening the retrofit cycle. Compared to traditional resistance coils that require periodic heating wire replacement, electromagnetic heating furnaces have no easily damaged heating elements and a lifespan of 5-10 years, significantly reducing downtime costs and maintenance burdens.
In practical applications, taking the plastic extrusion industry as an example, using an arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace can shorten preheating time by 30%-50%, reduce unit product energy consumption by 20%-40%, and significantly improve product dimensional stability and surface finish due to smaller temperature fluctuations. In food processing machinery, its clean and pollution-free heating method also better meets hygiene standards.
With the advancement of the national "dual-carbon" strategy and the optimization of industrial electricity pricing structures, the economic value of high-efficiency equipment is becoming increasingly prominent. Although the initial investment for arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces is slightly higher, their rapid return on investment through energy savings, stable process performance, and low maintenance costs have made them the preferred solution for energy-saving retrofits for many manufacturing enterprises.
In the future, with the widespread adoption of wide-bandgap semiconductor (such as SiC) inverter technology, electromagnetic heating power supplies will become smaller and operate at higher frequencies, further improving the response speed and control precision of arc furnaces. Furthermore, adaptive heating systems incorporating AI algorithms will enable the equipment to automatically optimize heating curves based on material characteristics. Arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces are quietly reshaping the future landscape of industrial thermal energy through the power of technology.
The core principle of the arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace is based on electromagnetic induction: when a high-frequency alternating current passes through an induction coil wound on an arc-shaped magnetic yoke, eddy currents are generated inside the metal load (such as a steel barrel) in front of it, thus directly converting electrical energy into heat energy. Because heat is generated inside the heated object, rather than through flames or resistance wires, heat loss is minimal, resulting in an energy utilization rate exceeding 90%, far higher than the 40%–60% of traditional resistance heating. Simultaneously, the entire process is flameless and produces no exhaust emissions, aligning with the development trends of green manufacturing and carbon neutrality.
The curved design is a key innovation of this type of equipment. The surface of a standard cylindrical workpiece is a continuous curved surface. Using a flat electromagnetic module would result in a gap between the coil and the cylinder wall, reducing magnetic coupling efficiency and potentially causing localized overheating or uneven heating. In contrast, the coil and yoke of the curved electromagnetic heating furnace are precisely pre-bent to the outer diameter of the cylinder, ensuring complete contact with the heated surface and maximizing the depth and uniformity of magnetic field penetration. This "tailor-made" structure not only improves heating efficiency but also reduces electromagnetic leakage, enhancing system safety.
In terms of material selection, arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces typically use high-permeability, low-loss nanocrystalline or ferrite cores as the yoke material, combined with high-temperature resistant mica plates, ceramic fibers, or silicone insulation layers to ensure electrical safety and structural stability during long-term operation above 300℃. The induction coils often use multi-strand Litz wire to effectively suppress the high-frequency skin effect, reduce AC resistance, and further improve energy efficiency. The outer casing is mostly made of aluminum alloy or stainless steel, combining heat dissipation, protection, and aesthetics.
The control system is also highly integrated. Modern arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces are generally equipped with intelligent temperature control modules that can collect the barrel temperature in real time and dynamically adjust the output power through PID algorithms to achieve temperature control accuracy within ±1℃. Some high-end models support multi-segment program settings, remote monitoring, fault self-diagnosis, and energy consumption statistics, facilitating integration with factory MES or industrial IoT platforms for digital management.
Ease of installation and maintenance is also one of the reasons for its popularity. Arc-shaped modules typically employ a segmented or snap-fit structure, allowing for quick installation onto existing equipment without disassembling the entire unit, significantly shortening the retrofit cycle. Compared to traditional resistance coils that require periodic heating wire replacement, electromagnetic heating furnaces have no easily damaged heating elements and a lifespan of 5-10 years, significantly reducing downtime costs and maintenance burdens.
In practical applications, taking the plastic extrusion industry as an example, using an arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnace can shorten preheating time by 30%-50%, reduce unit product energy consumption by 20%-40%, and significantly improve product dimensional stability and surface finish due to smaller temperature fluctuations. In food processing machinery, its clean and pollution-free heating method also better meets hygiene standards.
With the advancement of the national "dual-carbon" strategy and the optimization of industrial electricity pricing structures, the economic value of high-efficiency equipment is becoming increasingly prominent. Although the initial investment for arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces is slightly higher, their rapid return on investment through energy savings, stable process performance, and low maintenance costs have made them the preferred solution for energy-saving retrofits for many manufacturing enterprises.
In the future, with the widespread adoption of wide-bandgap semiconductor (such as SiC) inverter technology, electromagnetic heating power supplies will become smaller and operate at higher frequencies, further improving the response speed and control precision of arc furnaces. Furthermore, adaptive heating systems incorporating AI algorithms will enable the equipment to automatically optimize heating curves based on material characteristics. Arc-shaped electromagnetic heating furnaces are quietly reshaping the future landscape of industrial thermal energy through the power of technology.